 Asim Nath Dubey
Apr 01, 2025
Asim Nath Dubey
Apr 01, 2025

Accounting is more than just numbers. It serves as the foundation of every business, the universal language of finance, and an essential resource for individuals looking to manage their finances effectively.
Whether you're a student, a small business entrepreneur, or just interested in the flow of money, grasping the basics of accounting is crucial. This guide offers a thorough introduction to accounting, its core principles, and its significance for both businesses and individuals.
Accounting is the systematic recording, organizing, summarizing, and analyzing of financial transactions. It aims to present a transparent view of an organization's financial status, fostering clarity and supporting informed choices. In simpler terms, accounting helps you address questions such as:
Accounting is an essential practice that supports various sectors and individuals by offering a systematic approach to tracking financial transactions, managing budgets, and adhering to regulations. Here’s how people and organisation make use of accounting:
Accounting isn't just a back-office function; it's a strategic tool. Here's why it matters for businesses and individuals:
Use of Accounting for Businesses:
Use of Accounting for Individuals:
If you are an individual looking to gain insights into your day-to-day accounting activities, you must be aware of accounting practices. You can become a knowledgeable accountant yourself without really becoming a professional accountant. Here is a step-by-step guide on HOW TO BECOME AN ACCOUNTANT.
Grasping the basics of accounting is essential for understanding how financial data is monitored and presented. Here’s a straightforward overview of the key concepts you should familiarize yourself with:
|
Accounting Professionals |
Individuals who utilize these core concepts in their daily work, from bookkeeping to financial analysis. |
|
Accounting Software Developers |
Those who design tools that automate and simplify accounting tasks, helping businesses manage their financial information more efficiently. |
|
Financial Auditors |
Experts assess whether companies adhere to accounting standards and principles, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial reports. |
Mastering these fundamentals not only lays the groundwork for effective financial management but also improves your overall financial literacy.
Accounting has various branches that serve distinct purposes. There are eight major types of accounting. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of accounting.
1. Financial Accounting
Financial accounting is a branch of accounting that aims to provide an accurate and transparent overview of a company's financial performance over a certain time frame. This information is crucial for external parties like investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies who rely on it to make informed decisions.
Here are some key features of financial accounting:
Overall, financial accounting plays a vital role in maintaining transparency and trust among stakeholders by providing a clear and standardized method of reporting a company's financial activities.
2. Managerial Accounting
Managerial accounting equips you, as part of internal management, with essential financial insights to support informed decision-making in your business.
Key Features of Managerial Accounting include:
3. Cost Accounting
The main goal of cost accounting is to help you determine the actual costs of your goods or services, making it easier to budget and control expenses. By understanding these costs, you can make smarter pricing and financial decisions for your business.
Key Features of Cost Accounting Include:
4. Tax Accounting
Tax accounting is all about helping you manage and prepare your tax returns while ensuring you comply with tax laws. This helps you navigate the complex world of taxes so you can meet your obligations without unnecessary stress.
The Key Features of Tax Accounting are that it;
5. Auditing
Auditing is checking your financial statements for accuracy and compliance with standards. Auditing helps ensure that stakeholders can trust the information you provide about your financial health.
Key Features of Auditing include:
6. Forensic Accounting
Forensic accounting is the investigation of financial discrepancies and potential fraud. It combines accounting know-how with investigative skills to help uncover any financial wrongdoing.
The Key Features of Forensic Accounting are that it:
7. Government Accounting
Government accounting helps manage public funds and maintain accountability within government agencies. This ensures that your tax dollars are managed transparently and responsibly.
Key Features include:
8. Nonprofit Accounting
Nonprofit accounting is designed to help you track income, expenses, and funding for your nonprofit organization. It ensures that you can fulfill your mission while being accountable to your donors and stakeholders.
The Key Features of Nonprofit accounting are that it:
Each of these accounting types plays a crucial role in providing tailored financial insights for different stakeholders, helping you make informed decisions and manage your finances effectively
Understanding Accounting Principles and Standards helps you manage your company finances effectively wherever you are. Accounting principles are the foundational guidelines and rules that companies follow when recording and reporting financial data, while accounting standards are specific rules and procedures based on these principles, ensuring consistency and transparency in financial reporting.
Here are the key differences between Accounting Principles & Standards
|
What is it?
|
Accounting Principles |
Accounting Standards
|
| Accounting principles are the broad, underlying concepts and guidelines that form the basis for accounting practices. |
Accounting standards are specific rules and procedures that implement accounting principles.
|
|
| Purpose: | They provide a framework for classifying, recording, and interpreting financial data. |
They ensure consistency, comparability, and transparency in financial reporting across different companies and periods.
|
|
Examples
|
Accrual Principle: Transactions are recorded when they occur, not when cash changes hands. |
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS): A set of accounting standards used globally, issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
|
| Matching Principle: Expenses are matched with the revenues they help generate in the same accounting period. |
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP): A set of accounting standards used in the United States, developed by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
|
|
| Cost Principle: Assets are recorded at their original cost. |
Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS): The accounting standards followed in India.
|
|
|
Going-concern principle: The assumption that a business will continue operating in the foreseeable future.
|
||
|
Full Disclosure Principle: All relevant information must be disclosed in financial statements.
|
In the world of finance, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) are vital in creating and revising accounting standards that promote consistency and transparency in financial reporting.
For publicly traded companies, following these standards is key to gaining investor trust, as precise financial reporting enables better decision-making. At the same time, auditors act as careful overseers, examining financial statements to confirm compliance and accuracy. Collectively, these components enhance integrity in the financial sector, benefiting businesses, investors, and the overall economy.
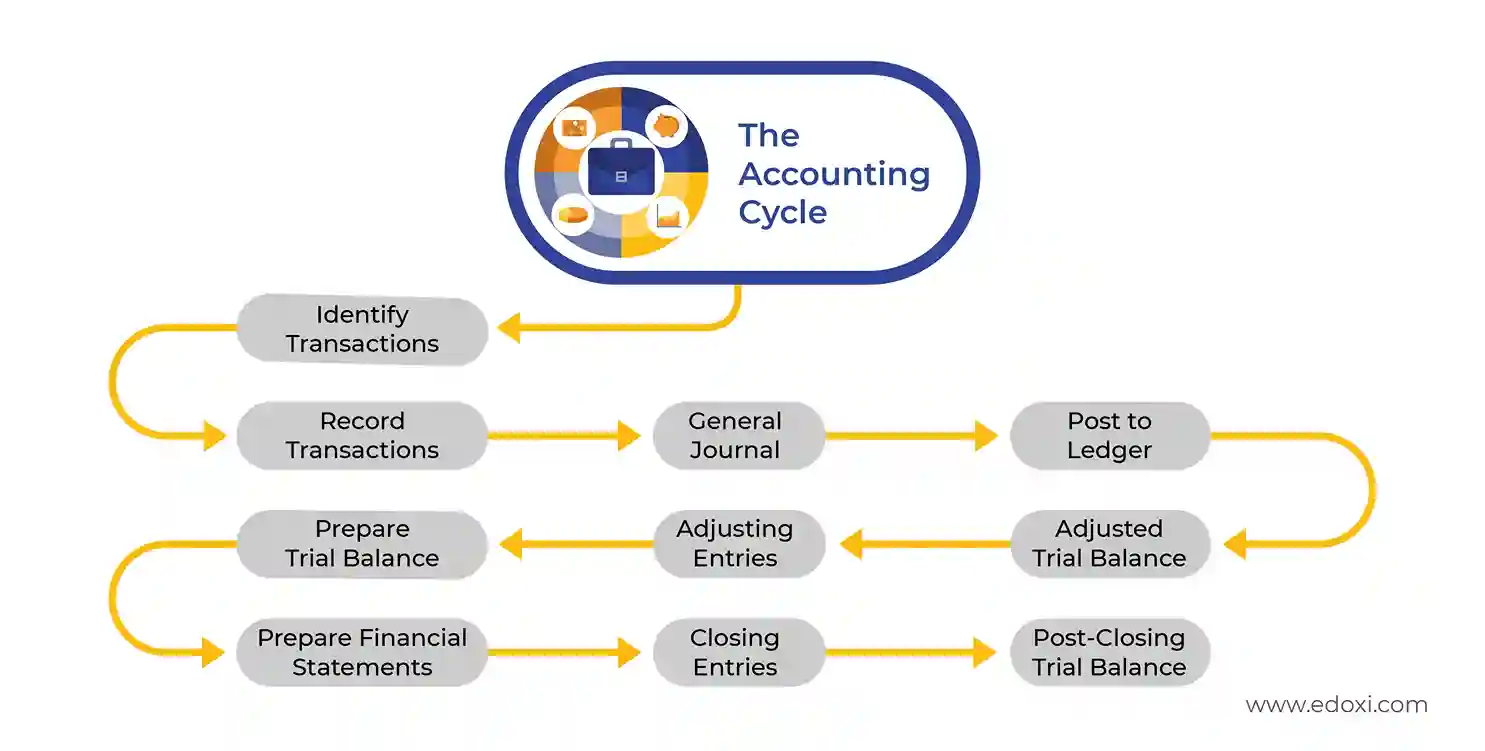
The accounting cycle is a series of steps that businesses follow to record and report their financial information. You might be interested to know how it works.
Here's a simplified visual representation of the accounting cycle:
Understanding financial statements is essential for anyone involved in business, including managers, investors, and creditors. By examining these documents, you can uncover valuable insights into a company's financial health, stability, and growth potential. Let’s explore the main financial statements and their importance:
Who Uses Financial or Accounting Statements?
There are several accounting methods and systems that businesses use to manage their financial records. Here are the most common accounting methods and systems used in the market:
There are also specialised accounting systems used in the industry. Some of these systems include
Which accounting method or system should you choose?
The choice of accounting method and system depends on various factors such as the size of the business, industry, complexity of operations, and specific financial reporting requirements.
In today’s digital age, various accounting tools and software play a crucial role in improving both efficiency and precision in financial management.
Important accounting tools and software consist of the following:
Starting a career in accounting means stepping into a key role that plays a significant part in the financial health of both businesses and individuals. As an accountant, you'll find yourself at the intersection of finance, compliance, and strategic planning. This job demands precision and high ethical standards, as you'll often be analyzing numbers and data to ensure that financial practices are effective and legally compliant.
Accounting matters in every industry, from small startups to large global corporations and even government entities. Although this career path provides numerous opportunities for growth and development, it can also come with its share of challenges, particularly when navigating complex regulations and the intricacies of financial management.
Accounting is one of the career fields that offers stability, growth, and personal satisfaction. Many career-seeking professionals are attracted to this field due to its numerous advantages. Here are some compelling reasons why a career in accounting can be a smart choice:
A career in accounting can offer stability, good income, diverse options, intellectual engagement, and ample opportunities for advancement, making it an attractive choice for many individuals. Here, you can explore the Advantages of An Accounting Career in detail.
An accountant is responsible for many activities, from preparing financial statements to analysing data, preparing tax returns, managing budgets, auditing records and more. As an accountant, your responsibilities will be varied and can include the following:
These are some of the major activities that an accountant is responsible to do. Here you may explore the roles and responsibilities of an accountant (another blog) in detail.
Accounting is a vast field that offers a diverse range of career opportunities to cater to various interests and skill levels. Businesses of all sizes nowadays rely on accurate financial information for decision-making. Therefore, the demand for skilled accounting professionals remains strong.
From traditional roles like public accountants and auditors to specialized positions in tax consulting and forensic accounting, the profession provides pathways for growth and advancement. Whether you are just starting or looking to advance your career, the accounting profession offers you plenty of opportunities. Let us check out these accounting careers
Here are some common job titles within the accounting field:
While, you may check out the top eight high paying accounting jobs here.
Remote Accounting Jobs
In today’s digital age, many accounting jobs can be performed remotely, offering flexibility and work-life balance. Some of the accounting jobs that can be performed remotely include:
In the ever-evolving field of accounting, obtaining a professional certification can significantly enhance your career prospects and establish your credibility in the industry. Numerous accounting certifications are available, and they serve as a testament to your knowledge, skills, and commitment to professional excellence. Whether you're just starting your career or looking to advance in your current position, understanding the top accounting certifications can help you make informed decisions about your professional development. Let's check out the major accounting certifications available for an aspiring accounting professional.
You may also find these 10 Best Accounting Certification Courses for Career Improvement.
Average Salaries of Accountants Worldwide:
Accountant salaries can vary quite a bit depending on where you are in the world. Based on data from 2024, here’s a snapshot of what accountants are earning in different regions:
These figures give a good overview of what to expect in the accounting field globally!
Average Salary of Accountants by Experience:
Accountants' salaries can vary quite a bit depending on their level of experience. Here is a categorisation of accountant salaries by experience levels.
Factors Influencing Salaries:
Several key factors can impact an accountant's salary, such as the following:
Global Demand:
There’s a steady demand for accountants across the globe, driven by more stringent regulations and the increasing complexity of financial transactions. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) anticipates a 6% growth in employment for accountants and auditors from 2021 to 2031, matching the average growth rate for all occupations.
Accounting Sector Job Trends:
Public accounting is flourishing as firms broaden their advisory services.
Here is a comprehensive guide to Accounting Salaries by job roles and countries and how to boost yours.
The job market for accountants in the UAE is strong, thanks to the country’s growing economy and diversification into sectors like tourism, trade, and finance. Cities like Dubai and Abu Dhabi are particularly active, with many financial services companies looking to hire. There’s also a heightened focus on compliance and risk management as businesses adapt to new economic regulations and tax laws like VAT.
If you're looking to build a career in accounting in the UAE, there are plenty of opportunities out there!
Accountants are essential for keeping financial records in order and ensuring that regulations are followed. Because of this, they must possess a variety of specific skills. Here are some key skills that every accountant should have:
Technical Skills
Analytical Skills
Mathematical Skills
Technology Proficiency
Communication Skills
Organizational Skills
Problem-Solving Skills
Ethical Judgment
Teamwork
Continuous Learning
Here are the top technical Accounting Skills you must have to succeed in your career.
Mastering these skills not only helps you excel at your job but also supports your career development.
Before diving into complex concepts, familiarize yourself with basic accounting principles. Understanding terms like assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses is crucial.
Strategies for Learning
As you progress, focus on more complex subjects such as taxation, auditing, and managerial accounting. Explore the following strategies:
Preparing for accounting exams requires a structured approach. From creating a study schedule that allocates specific times for studying to breaking down topics into manageable sections, here are some effective strategies to help you prepare for your accounting exam.
When you're thinking about enrolling in an accounting course, keep these important factors in mind:
By weighing these factors, you’ll be better prepared to choose the right accounting course for your needs!
Choosing a career in accounting can feel overwhelming, but breaking it down into simpler steps can make it easier. Here, we can help you figure out the best path for you.
By considering these factors, you can make smart decisions about your education and career in accounting that align with your interests and aspirations.
Choosing the right accounting training institute is a crucial step on your path to a successful career in accounting. With so many options available, it's important to take some time to evaluate different factors to make sure you choose wisely. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind as you explore your options:
Taking these considerations into account can help ensure that you select an accounting training institute that aligns with your goals and supports your journey.
In Dubai, several accounting training institutes stand out due to their quality of education and comprehensive training programs. Here’s a comparative analysis of some of the leading institutes:
| Institute Name | Course Offerings | Pricing | Location | Accreditation |
| London School of Business and Finance (LSBF) | ACCA, CIMA, CPA, IFRS, etc. | Varies based on the course; typically starts around AED 4,500 | Dubai Marina |
ACCA, CIMA, CPA
|
| Edoxi Training Institute | ACCA, CIMA, CPA, IFRS, CMCA, Finacial Acconting, +30 more | Varies based on the course | Dubai, Next to Burjuman Metro Station Exit 3 | KHDA, QA QC |
| The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) | CA, Diploma in International Taxation | AED 5,000 - AED 10,000 | Jumeirah Lake Towers | ICAI |
| EduPristine | ACCA, CPA, CMA, IFRS, Financial Modeling | Approx. AED 3,500 - AED 8,000 | Dubai Internet City | ACCA |
| Emirates Academy of Hospitality Management | Hospitality Accounting and Finance courses | Starts around AED 6,000 | Near Burj Khalifa | CTH |
| Goldsmiths, University of London | BSc in Accounting and Finance | Roughly AED 18,000 a year | Downtown Dubai |
University of London
|
When selecting an accounting training institute, take the time to research and compare different options based on reputation, faculty, course offerings, support services, and the success of alumni. By understanding your career goals and assessing each institute against these factors, you can choose a program that will set you up for success in the accounting field.
Technology has changed the way we handle accounting, providing us with tools that make our work faster and more accurate. Let’s take a closer look at how this shift is happening.
Technological Impact
The influence of technology on accounting is transforming how businesses handle their finances. Here are some of the key changes we've seen:
Today’s accounting practices are being transformed by several key developments:
If you’re on the hunt for accounting software, there are several great options out there that cater to different needs:
If you are interested to know What is QuickBooks? How Does It Work? check it out here. You can also get professional training in QuickBooks.
Learn Xero and get Xero Certified from a professional accounting training institute in Dubai.
These options each come with their strengths and are suited to different types of users, so it’s worth considering your specific needs when choosing the right software.
The impact of AI and automation on accounting is significant, reshaping how the industry operates. Here’s how:
Here, you may check out how AI & Automation are changing accounting profession at differents levels. These technologies not only boost productivity but also transform the accountant's role from number crunching to valuable business strategy.
When it comes to choosing between cloud-based and traditional accounting systems, there are a few key factors to keep in mind:
Technology is revolutionizing the way accounting is done, enhancing efficiency and allowing accountants to provide more valuable insights and advisory services. As you explore your options in this changing landscape, keeping these factors in mind will help you make smart decisions that align with your accounting needs.
The future of accounting is poised for transformation, driven by several crucial factors, including technology, the ever-changing regulatory landscape, and evolving business demands. Let’s explore these elements and what they mean for the accounting profession:
Technological Advancements
Changing Business Needs
The accounting profession is evolving rapidly in response to these factors. To thrive, accountants will need to embrace new technologies, stay updated on regulatory changes, and develop skills that align with modern business demands. This evolution positions accountants as strategic partners, helping businesses navigate the complexities of today’s landscape.

Asim Nath is an Accounting and Microsoft Office trainer at Edoxi Training Institute. He has over 13 years of training experience and has successfully trained more than 3000 professionals in Accounting and Microsoft Office applications. Asim’s specialisations include Financial Accounting, Tally, Zoho and Quickbooks. His background in financial accounting adds valuable insights to business presentation training.
Asim is an expert in MS Office, including PowerPoint, Excel, and Power BI, positioning him as a well-rounded specialist in the Microsoft Suite. Asim employs a practical, business-focused teaching methodology. His one-to-one training approach ensures each student receives personalized attention. He emphasizes real-world applications, helping professionals create impactful business presentations.