 Satendra K
Aug 21, 2025
Satendra K
Aug 21, 2025

“Cybersecurity is vital for maintaining the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information. As more devices connect to the internet, the attack surface for potential threats expands, making cybersecurity a priority for all sectors.”
Cybersecurity involves safeguarding systems, networks, and programs against digital threats that seek to access, modify, or destroy sensitive data. It encompasses a mix of technologies, processes, and policies to prevent cyberattacks or reduce their effects.
In today's digital world, businesses, governments, and individuals depend on technology and the internet, making them vulnerable to various threats like:
According to recent cybersecurity statistics, “a cyber attack occurs roughly every 39 seconds globally, with an average of 2,200 attacks daily. “
The global cybercrime damage is predicted to reach a staggering $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, signifying the widespread impact of cyber threats.
This highlights the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures today. The cost of data breaches is significant, with ransomware attacks being a major concern.
The increase in cyberattacks and data breaches underscores the need for strong cybersecurity measures, including:
Recent data breaches highlight that no one company, big or small, is immune. This reality emphasises the urgent need for robust protection strategies, continuous security awareness training, and incident response plans to mitigate risks and safeguard digital assets against evolving cyber threats.
Check out these Reasons why Cybersecurity is now important more than ever.
Let’s check out why cybersecurity important for different groups of people like students, working professionals, business owners, organisations, tech enthusiasts and policymakers.
Cybersecurity encompasses several fundamental areas, often referred to as the core pillars. These can also be called Types of Cybersecurity. These pillars provide a framework for protecting digital assets from various threats and vulnerabilities. By concentrating on key aspects, organizations can establish strong defences to ensure data integrity and continuity.
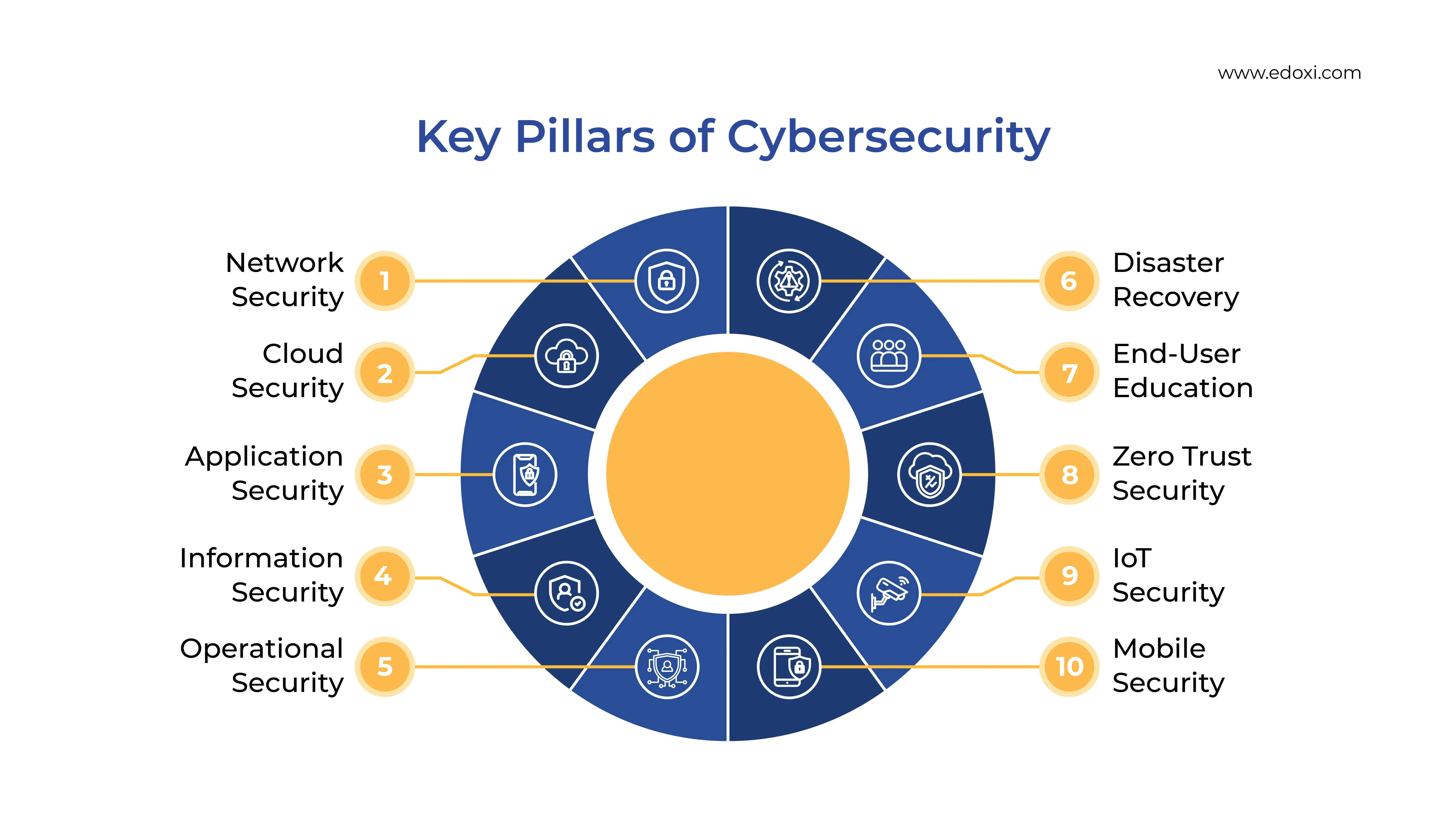
Network security involves implementing measures to protect the integrity, usability, and safety of the network and data. This includes using firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and virtual private networks (VPNs) to safeguard against unauthorised access and cyber threats.
Companies like Cisco and Fortinet specialise in providing network security solutions to help organisations secure their infrastructure. Taking Network Security Courses will help you learn what best measures should be implemented to protect your organisation’s network.
Cloud security protects information through encryption, which codes data to prevent unauthorized access. It includes identity and access management to control user access and verify identities. Network security also defends against threats like hacking and malware using tools like firewalls.
Cloud Security Courses like Certified Cloud Security Engineer (CCSE) or Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) can help you become an in-demand cloud security professional.
Application security encompasses the processes and tools used to protect applications from threats throughout their lifecycle. This involves coding practices, security testing, and regular updates to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Organisations often rely on platforms like OWASP for guidelines and tools to enhance the security of their software applications. Here you can learn more about Application Security and the possibilities of Application Security Courses.
Information security focuses on protecting data from unauthorised access, disclosure, alteration, and destruction. This includes implementing access controls, encryption, and data loss prevention strategies to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
Companies like Symantec and McAfee offer solutions that help organisations safeguard their data assets.
Operational security (OpSec) protects critical processes and sensitive assets vulnerable to unauthorised access and exploitation. It involves assessing risks related to both people and processes, ensuring that operational practices minimise the chance of breaches.
Businesses often utilise frameworks provided by organisations like NIST to establish robust operational security plans.
Disaster recovery and business continuity planning involves preparing for the recovery of IT infrastructure and operations after a cybersecurity incident. This includes developing detailed strategies for data backup, system restoration, and maintaining service availability during an outage.
Companies like IBM and VMware provide solutions that help organisations create effective disaster recovery plans. Whether an individual or an organisation, get Incident Handling Training to get yourself prepared to handle any cybersecurity incidents.
End-user education is critical in empowering individuals to recognise and respond to cybersecurity threats effectively. Training programs help users understand the risks associated with phishing, social engineering, and other attack vectors, fostering a security-aware culture within the organisation.
Training Institutions like Edoxi often deliver engaging and informative training on Security Management Courses.
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity model that assumes threats can come from both outside and inside the network. It requires continuous verification of users and devices through strict authentication, least privilege access, and micro-segmentation.
Companies like Microsoft and Palo Alto Networks offer solutions to implement Zero Trust frameworks.
IoT Security focuses on protecting Internet of Things devices from cyber threats. This involves secure device authentication, data encryption, regular software updates, and threat detection to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Solutions from companies like Cisco and Check Point help secure IoT ecosystems.
Mobile Security involves protecting organizational data accessed through mobile devices. Key practices include data encryption, Mobile Device Management (MDM), app security, and user training against threats.
Vendors like VMware and MobileIron provide tools for effective mobile security strategies.
By prioritizing these areas, organizations can build robust defences to protect their digital assets effectively.
Read Also : Top Cybersecurity Training Companies in Sydney, Australia
Cybersecurity threats are diverse and continually evolving, posing significant risks to individuals and organisations. Understanding these threats is essential for developing effective security measures. Below are some common types of cybersecurity threats:

Cybersecurity works through a multi-layered strategy that combines technology, processes, and policies. Key parts of this strategy include:-
Organizations actively engage in continuous monitoring, threat detection, and response efforts, leveraging advanced technologies and best practices to maintain a robust cybersecurity posture.
Now, let’s check out the top tools and technologies used in Cybersecurity.
Top tools and technologies for cybersecurity include:
These tools are essential for creating a robust cybersecurity posture, safeguarding sensitive information, and maintaining overall network integrity.
A Cybersecurity professional must know how to use these tools and technologies effectively. If you are an expert in these cybersecurity tools and technologies, there are plenty of career opportunities awaiting you in the global job market.
Career opportunities in cybersecurity are appealing, especially with the increasing demand for protection against cyber threats. Professionals in the cybersecurity area can explore roles across various sectors, including government, finance, healthcare, and technology, each requiring specialized skills and knowledge. As cyber threats continue to evolve, you can expect opportunities in this field to grow significantly.
Based on the latest Cybersecurity Job trends, the following are some of the in-demand cybersecurity job roles.
In-Demand Cybersecurity Roles You Might Consider:
Some of the highest-paid cybersecurity roles globally include:
To succeed in a cybersecurity career, you will require the following skills.
Cybersecurity certifications offer numerous advantages that can significantly impact your career trajectory. They validate your expertise, boost your credibility, and enhance your job prospects in a competitive market.
Whether you are looking to land a new job or climb the corporate ladder, these certifications can set you apart from rivals and help you access specialized roles that lead to greater career advancement opportunities.
In the current digital environment, obtaining top cybersecurity certifications such as CISSP, CEH, and CompTIA Security+ is crucial for professionals aiming to enhance their expertise and maintain a competitive edge.
These certifications address vital topics, including threat management, ethical hacking, and risk assessment, providing individuals with the essential knowledge needed to defend against cyber threats effectively. Acquiring these credentials not only enhances career prospects but also showcases a dedication to protecting digital assets.
Whether you are entering the cybersecurity field or are a seasoned expert, recognizing the importance of these certifications can significantly inform your professional development choices in this rapidly changing industry.
The CEH certification from the EC-Council trains you to think like a hacker (ethically) to pinpoint system vulnerabilities. It covers penetration testing tools and techniques, making it essential for careers in cybersecurity auditing, network engineering, and defense analysis. By understanding the hacker mindset, you can proactively defend systems against potential attacks. If you want to become an Ethical Hacker, here is how to become a Certified Ethical Hacker.
If you're moving into management within information security, the CISM is for you. This certification emphasizes aligning information security with business goals, risk management, and governance. Earning your CISM enhances your credibility as a security manager and demonstrates your capability to lead an enterprise’s security program effectively. Here’s how to become a Certified Information Security Manager.
For advanced security professionals, the CISSP is ideal. It covers a comprehensive framework of information security topics, including risk management and security architecture. Obtaining a CISSP can significantly boost your reputation and position you for leadership roles in cybersecurity. Here’s a guide on how to become a Certified Information Systems Security Professional.
If you want to know CISSP Certified Professional Jobs and Salary, here is a complete career graph.
You can also check out the Potential career paths to follow after passing CISSP.
The CompTIA CASP+ certification is aimed at experienced cybersecurity engineers seeking to deepen their expertise without moving into management. It covers enterprise security, risk management, and advanced security solutions, validating your skills in tackling complex security challenges.
The Certified Infrastructure Tester offered by CREST focuses on identifying network vulnerabilities and conducting security assessments. This certification enhances your technical proficiency in vulnerability assessment, making you a valuable asset in securing network infrastructures.
If you're working within AWS environments, the AWS Certified Security — Specialty certification validates your ability to secure data and applications in the cloud. It teaches risk management, incident response, and infrastructure security, equipping you for security in complex cloud environments. If you’re looking for a job in Dubai in AWS security, here is a guide on how to become an AWS Certified Professional in Dubai.
The CISA from ISACA is designed for those involved in auditing and ensuring the integrity of information systems. This certification enhances career prospects in audit and compliance roles, reflecting your competence in information system governance. If you are looking for a CISA job opportunity in UAE, here is a brief overview of the Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) Salary in UAE.
The CCSP certification by ISC2 is tailored for cloud professionals, focusing on cloud security architecture, governance, risk management, and compliance. This certification is essential as organizations increasingly adopt cloud solutions, ensuring robust security in cloud deployments.
Each of these certifications expands your credibility and career opportunities across various sectors within cybersecurity.
To enter the field of Cybersecurity and to become a cybersecurity professional, follow these key steps:
If you need additional guidance, here is a step-by-step guide on how to become a Cyber Security Professional.
The cybersecurity landscape is rapidly evolving, especially in regions like Dubai and the wider UAE. Key to this evolution is the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, with predicted global cybercrime costs reaching $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. Amidst this rise in threats, the growing cybersecurity skills gap is becoming evident, recognizing the need for action to ensure effective defense mechanisms are in place.
In Dubai, the 2023 Cybersecurity Strategy aims to enhance resilience against digital threats, reflecting a commitment to becoming a global cyber hub. The city witnessed a 65% increase in cyber incidents in 2022 alone, underscoring the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures. 2025 Cybersecurity Job Trends & Opportunities in Dubai, indicates that the city is a rising hub for cyber security jobs.
Emerging technologies, like Artificial Intelligence (AI), are double-edged swords; while they enhance threat detection, they also enable more sophisticated attacks. Meanwhile, the looming advent of quantum computing poses a potential risk to current encryption methods, necessitating a shift toward quantum-resistant algorithms.
Here’s a whitepaper that discusses cybersecurity career trends and job opportunities in the Middle East for 2025. It highlights key trends, particularly in the UAE, which is significantly investing in cybersecurity awareness and education. Reports indicate a projected 40% increase in cybersecurity jobs by 2026. As businesses adjust to remote and hybrid work models, ongoing training and upskilling of cybersecurity professionals will be essential to protect against evolving threats.
In summary, Dubai and the UAE are at the forefront of adapting to future cybersecurity challenges while promoting innovation and resilience.

Chief Technology Officer & Cyber Security Expert Trainer
Satendra Singh Khari is a renowned cybersecurity expert and the Chief Technology Officer at Edoxi, where he leads the CEH v13 AI program. With over 12 years of experience, he has trained more than 10,000 professionals and earned recognition in the Circle of Excellence for 2023 and 2024. Mr. Khari holds multiple industry certifications, including CISSP, CISM, CEH, CPENT, and CREST, which showcase his expertise in vulnerability assessment, penetration testing, and incident handling.
His practical insights, gained during his tenure as Head of Information Security in Malaysia, enhance the learning experience by providing students with essential technical skills and a clear path to career advancement. Recognized as a leader in his field, he has received the Internet 2.0 Outstanding Leadership Award for three consecutive years (2022-2024), reflecting his dedication to empowering the next generation of cybersecurity professionals.