Our CompTIA A+ Certification Course is a 40-hour comprehensive online program designed to equip you with the foundational skills needed to launch a career in IT. As an official CompTIA delivery partner, we offer a high-quality, structured learning experience that covers the essential areas of hardware, software, networking, and cybersecurity. Whether you're new to IT or switching careers, our Online CompTIA A+ course provides the practical knowledge and confidence to pursue entry-level IT roles and pass the CompTIA A+ certification exams.
Through real-world examples and hands-on labs, you’ll learn how to install, configure, troubleshoot, and maintain IT systems across various platforms. You’ll also gain essential experience in diagnosing common issues and applying industry-standard best practices in IT support.
Here’s What You’ll Learn from the CompTIA A+ Certification Training Online:
Our CompTIA A+ course is ideal for anyone looking for flexible, high-quality IT training that leads to real career opportunities. Delivered by industry experts, the training aligns with the latest CompTIA A+ certification requirements and offers global relevance.
You'll benefit from expert-led sessions, hands-on experience, and access to exam-focused resources– all in a format that fits your schedule and pace. This course is ideal for anyone looking for flexible, high-quality IT training that leads to global career opportunities.
Delivered by our experienced IT professionals, the program aligns with the latest CompTIA A+ certification requirements and provides a perfect balance of theory and hands-on practice.
As an official CompTIA-authorized training provider, we ensure expert-led instruction, up-to-date curriculum, and exam-focused resources that help you stay on track. The online format allows you to learn at your own pace and access materials anytime, from anywhere in the world.
Whether you're a beginner or someone looking to enter the IT field, the course requires no prior experience and is designed to build your confidence from the ground up.
Upon completion, you’ll be equipped with the skills and knowledge to qualify for in-demand IT roles and increase your credibility and earning potential in today’s tech-driven job market.
| Exam Criteria | Details |
| Exam Codes |
|
| Duration | 90 minutes per exam |
| Number of Questions | Up to 90 per exam |
| Question Types | Multiple choice, drag-and-drop, performance-based |
| Passing Score |
|
| Exam Fee | USD 253 (plus taxes) per exam |
| Validity | 3 years from the date of certification |
You’ll learn how to build and troubleshoot a complete computer from scratch using real hardware tools and system utilities. This practical experience helps you understand how every component works together.
You’ll practice installing and setting up Windows step by step, with basic exposure to Linux and macOS, so you're confident working across different platforms.
You’ll configure networks using tools like ipconfig and learn how to work with routers, switches, and firewalls to build secure and reliable connections.
You’ll solve common IT problems through real-life examples, including hardware failures, software glitches, and network issues, preparing you for actual job environments.
You’ll gain hands-on experience using antivirus software, firewalls, and encryption methods to protect systems and data–key skills every IT professional needs.
You’ll receive well-organized PDF study guides that cover everything you need for both the Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) CompTIA A+ exams.
If you're looking to start a career in IT support or system administration, this course gives you the right foundation.
Just finished school or university? This is a great way to enter the technology field and gain job-ready skills.
Thinking of moving into IT from another field? If you understand basic computer operations, you’re ready to begin.
Already working in helpdesk or support roles? This certification can validate your skills and open doors to higher roles.
Love working with computers or solving tech problems? This course will expand your knowledge of hardware, software, and networking.
Planning to pursue certifications like Network+ or Security+? A+ is the perfect first step in your certification path.
Our CompTIA A+ course includes hands-on projects that help you apply what you’ve learned in real-life scenarios. These projects are designed to build your confidence and technical skills:
You will involve in putting together a working computer using separate parts like the motherboard, CPU, RAM, and hard drive. You’ll also learn how to organize cables and test the system to make sure it works properly.
You will create a simple network for a small office. This includes connecting devices, setting up routers and switches, and making sure the Wi-Fi works smoothly.
You will practice installing Windows or Linux on a computer. You’ll also learn how to add drivers, adjust security settings, and make the system ready for daily use.
You’ll learn how to identify and fix common hardware problems using step-by-step diagnostic techniques.
You’ll practice installing and configuring both Windows and Linux operating systems, from basic setup to full deployment.
You’ll get hands-on experience with IP addressing, subnetting, and setting up basic network connections between devices.
The CompTIA A+ certification is a globally recognized credential that prepares you for a successful career in IT. It builds your core knowledge and practical skills in areas like hardware, software, networking, troubleshooting, and cybersecurity basics. Whether you're aiming for your first IT job or planning to move into a more technical role, CompTIA A+ gives you a solid foundation to build a long-term career in IT– anywhere in the world. Completing this course helps you:

Get expert assistance in getting your CompTIA A+ Course customised!
Here’s a four-step guide to becoming a certified CompTIA A+ professional.
Join Edoxi’s CompTIA A+ Course
If you're looking to start or grow your IT career, Edoxi offers a trusted and practical pathway to earn your CompTIA A+ certification. Our training is designed for learners worldwide who want real skills, expert support, and recognized credentials.
We are an official CompTIA training provider, offering a curriculum aligned with the latest Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) exam objectives.
Our course is built around real-world practicals, including PC building, network setup, and troubleshooting exercises to help you apply what you learn.
We provide clear guidance and learning resources that are ideal for beginners, students, and career changers looking to break into the tech field.
Study your way—whether online, in the classroom, or through corporate training. Our 40-hour program is designed to fit around your schedule and needs.
Learn from certified IT professionals with real-world experience in system administration, hardware support, networking, and security.
Get full support to register, prepare, and practice for your CompTIA A+ certification exams, including mock tests, exam strategies, and international testing guidance.

Our mentors are leaders and experts in their fields. They can challenge and guide you on your road to success!

Sid Ahmed
Sid Ahmed is an IT network infrastructure and security trainer with over 12 years of experience at Edoxi Training Institute, Dubai. He is a certified CCNA/CCNP instructor and NSE 4 trainer and possesses advanced expertise in Cisco networking His portfolio includes prestigious Cisco certifications and hands-on knowledge of global security frameworks, making him a leader in delivering industry-relevant training.
Sid’s knowledge also extends to industry standards such as ISO 27001, NIST, SOC2, and PCI DSS, further strengthening his cybersecurity prowess.Sid Ahmed focuses on developing practical skills through hands-on training with enterprise-grade equipment. As an experienced Network and Security Architect, Sid Ahmed's expertise spans WAN/LAN, IP-MPLS, BGP, Wireless, IP Telephony, and Cybersecurity.He is skilled in HLD/LLD design, audits, pentesting, IT risk assessments, and security frameworks His specialisations include SD-WAN, VPN, VLAN, SSL, SIEM, cloud tech, and routing protocols (OSPF, BGP, STP) Sid is also proficient in Python, MySQL, JavaScript, APIs, and tools like SolarWinds, FortiSIEM, and U2000.
Here is the list of other major locations where Edoxi offers CompTIA A+ Certification Course
You'll build practical, job-ready skills. The course covers:
Our hands-on labs and guided projects ensure you learn by doing, not just theory.
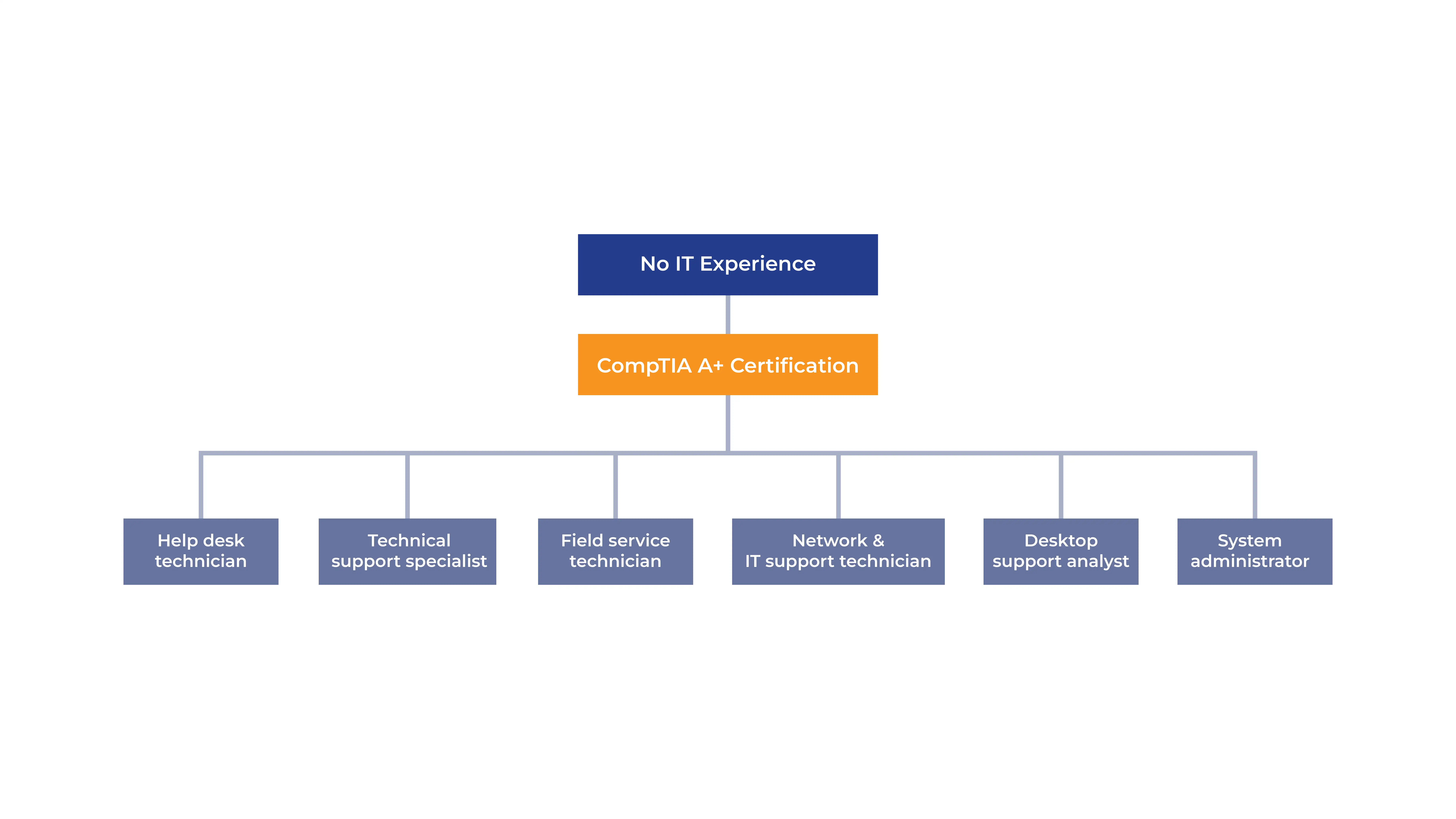
Once certified, you'll be ready for in-demand roles such as:
The certification is recognized worldwide and acts as a stepping stone to mid- and senior-level roles in networking, systems administration, and cybersecurity.