The EC Council's Certified Ethical Hacker v13 program is the first ethical hacking course worldwide to use AI. Edoxi provides you 40-hour online CEH v13 course along with hands-on-training expeience.
We will deliver the CEH v13 course integrating AI into all five stages of ethical hacking. This includes;
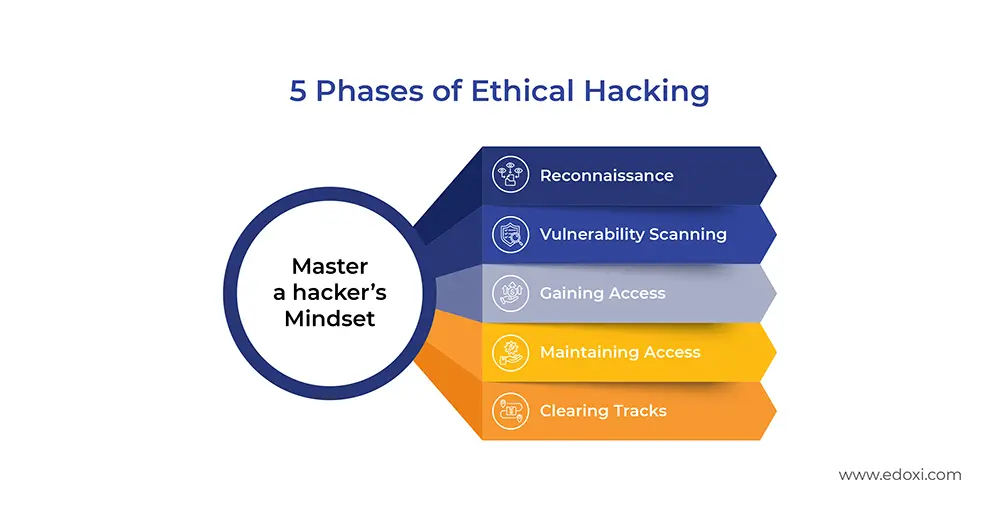
You can experience this AI Revolution in Ethical Hacking as a Certified Ethical Hacker in Version 13 with Edoxi. As an EC Council Authorized Training Center, Edoxi offers the CEH v13 course along with various other Cybersecurity Courses.
Edoxi will assist you in gaining the skills required to navigate the advanced landscape of cybersecurity as a Certified Ethical Hacker, trained in the most recent version of CEH v13 that is powered by AI.
Our trainers, who are industry-experienced and certified in cybersecurity, will equip you with AI-enhanced tools and methods to identify, exploit, and protect against vulnerabilities in systems and networks.
Our CEH v13 AI Course, guided by our cybersecurity professionals, will assist you in:
Our training incorporates state-of-the-art AI tools from EC-Council’s latest CEH v13 curriculum, boosting your ethical hacking proficiency. These tools are detailed along with its application in the table below.
| AI Tool | Application in Ethical Hacking |
| ShellGPT |
|
| ChatGPT |
|
| FraudGPT |
|
| WormGPT |
|
| DeepExploit |
|
Our Certified Ethical Hacking Course equips you with knowledge of different hacking methods and techniques. We grant you the capacity to adopt a hacker's mindset while upholding suitable ethical principles.
With an in-depth curriculum, practical labs, and real-world project experiences, you will cultivate a thorough skill set in AI to conduct efficient penetration testing, evaluate the security stance of systems, and reduce possible attacks.
| Benefit Category | Details |
| Exam Voucher | Discounted pricing from EC-Council for Edoxians (Standard price: USD 1,199) |
| Study Materials | Complete EC-Council digital courseware access |
| Practical Exam | Discounted pricing from EC-Council for Edoxians |
| Additional Certificate | Industry approved course completion certificate |
Upon completing our Certified Ethical Hacker Course, you'll have the opportunity to demonstrate your skills through online practical assessments, which include a 4-hour Knowledge-Based Exam and a 6-hour Practical Exam.
| Component | Knowledge-Based Exam | Practical Exam (Optional) |
| Exam Code | 312-50 (ECC/VUE) | Via ASPEN iLabs |
| Exam Duration | 4 Hours | 6 Hours |
| Format | 125 multiple-choice question | Hands-on practical assessments |
| Passing Criteria | 60%–85% (varies by question weight) | At least 50% of practicals completed |
| Certification | CEH v13 | CEH Master designation |
| Validity | 3 years | 3 years |
| Recertification | 120 CECs or retake exam | 120 CECs or retake exam |
Experience hands-on training on the EC-Council's iLab platform, where you can safely practice in secure environments featuring live networks and authentic vulnerabilities.
Participate in realistic scenarios that replicate current threats, including advanced persistent threats (APTs), malware attacks, and network breaches, helping you cultivate essential cybersecurity skills.
Engage in structured exercises like password cracking and exploit testing. You'll gain access to AI-powered tools for effective vulnerability scanning and malware analysis.
Learn both offensive and defensive strategies to efficiently secure systems and mitigate a variety of potential threats.
Study significant cyberattacks to uncover vulnerabilities, understand attack methodologies, and devise effective response strategies.
Acquire the knowledge to identify, analyze, and respond to cybersecurity incidents using advanced methodologies and tools.
Return to EC-Council's iLab platform, which features live networks and unpatched systems, allowing you to conduct vulnerability analyses and penetration tests in a controlled environment.
Tackle real-world challenges, such as managing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and implementing Zero Trust Architecture.
Engage in role-playing exercises as both attackers and defenders while analyzing historical cyberattacks to enhance your skills in threat detection and incident response.
Become proficient in utilizing tools like Nmap, Nessus, and Wireshark for network scanning. You'll also perform vulnerability assessments with Burp Suite, Acunetix, and OWASP ZAP.
Leverage cutting-edge tools such as ShellGPT for penetration testing, FraudGPT for threat detection, and DeepExploit for conducting vulnerability assessments.
Conclude the course by completing real-world projects focused on penetration testing, malware analysis, cloud security, IoT assessments, and incident response.
Those managing networks and systems to detect vulnerabilities and secure IT infrastructure through ethical hacking.
Individuals focused on protecting digital systems to deepen their knowledge of hacking techniques and defensive strategies.
Those entering the IT field to build a strong foundation in cybersecurity and gain a competitive edge with CEH certification.
Professionals from non-IT backgrounds to transition into the growing cybersecurity field by acquiring practical ethical hacking skills.
Developers looking to learn how to code securely by understanding how attackers exploit software vulnerabilities.
Professionals responsible for assessing system security to benefit from understanding hacking methodologies and risk mitigation.
Edoxi’s CEH v13 course offers immersive, hands-on training designed to build real-world cybersecurity skills. Through advanced labs and guided projects, you’ll gain practical experience using the latest tools and techniques in ethical hacking.
You will gain access to EC-Council’s iLab platform with live networks and unpatched systems to safely perform vulnerability scans and penetration tests.
You will tackle real-world cybersecurity tasks like managing SIEM systems and applying Zero Trust Architecture principles.
You will experience both attacker and defender roles while studying real cyber-attacks to sharpen your detection and response skills.
You will learn to use tools like Nmap, Nessus, Wireshark, Burp Suite, Acunetix, and OWASP ZAP for scanning and vulnerability assessment.
You will explore cutting-edge tools such as ShellGPT, FraudGPT, and DeepExploit for AI-driven penetration testing and threat detection.
You will complete hands-on projects in malware analysis, IoT security, cloud infrastructure testing, and incident response planning.
The Certified Ethical Hacker v13 AI certification offers a gateway to a variety of career paths in the ever-evolving technology sector worldwide. Completing the CEH v13 course opens up numerous roles within the cybersecurity domain, each tailored to different interests and expertise. Here are the key outcomes and career opportunities following the CEH v13 course:

Get expert assistance in getting your CEH v13 Course customised!
Here’s a four-step guide to becoming a certified CEH v13 professional.
Join Edoxi’s CEH v13 Course
At Edoxi, we are dedicated to providing outstanding cybersecurity education that meets the needs of learners worldwide. Here are several reasons why organizations around the globe select us for their cybersecurity training:
Our structured learning approach, expert guidance, and hands-on practice ensure you are well-prepared to ace the CEH certification exam. We equip you with all the resources necessary for your success.
Take advantage of our discounted CEH exam vouchers and special rates for practical certification exams, allowing you to save considerably as you advance your career.
Experience an unparalleled learning journey with our advanced cloud labs. They provide engaging real-world scenarios, expose you to various vulnerabilities, and include pre-configured security tools that reflect industry standards.
Our courses align with the official EC-Council curriculum and are enhanced with state-of-the-art AI tools, practical exercises, and expert instruction. We are committed to supporting you every step of the way.
Join over 10,000 professionals who have benefited from our training, consistently achieving success in certifications and career advancement.
Edoxi is the training partner of choice for major organizations, including UAE Federal Government, Emirates Digital Wallet, Saudi Aramco, Australian Embassy, Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, Nigerian Government (Ministry of Foreign Affairs), The Supreme Council for National Security.

Our mentors are leaders and experts in their fields. They can challenge and guide you on your road to success!

Satendra K
Satendra Singh Khari is a renowned cybersecurity expert and the Chief Technology Officer at Edoxi, where he leads the CEH v13 AI program. With over 12 years of experience, he has trained more than 10,000 professionals and earned recognition in the Circle of Excellence for 2023 and 2024. Mr. Khari holds multiple industry certifications, including CISSP, CISM, CEH, CPENT, and CREST, which showcase his expertise in vulnerability assessment, penetration testing, and incident handling.
His practical insights, gained during his tenure as Head of Information Security in Malaysia, enhance the learning experience by providing students with essential technical skills and a clear path to career advancement. Recognized as a leader in his field, he has received the Internet 2.0 Outstanding Leadership Award for three consecutive years (2022-2024), reflecting his dedication to empowering the next generation of cybersecurity professionals.
Here is the list of other major locations where Edoxi offers CEH v13 Certification Course