 Maria Mehwish
Sep 11, 2025
Maria Mehwish
Sep 11, 2025
A cybersecurity career path opens diverse opportunities, starting with entry-level roles like Security Analyst or IT Auditor and advancing to mid-level positions such as Security Engineer or Incident Responder. With experience and skills, professionals can progress to senior leadership roles like Security Architect or Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). Along with a background in IT or computer science and certifications like CISSP, CEH, or CompTIA Security+, you’ll find yourself building a rewarding career in one of today’s most in-demand fields.
If you’re planning to step into the world of cybersecurity, this guide will walk you through the complete career path including key roles, must-have skills, educational pathways, certifications, and strategies for growth. Whether you’re a student exploring options, an IT professional considering a shift, or an experienced specialist aiming for leadership, you’ll find practical insights to help you thrive in this fast-evolving and rewarding field.
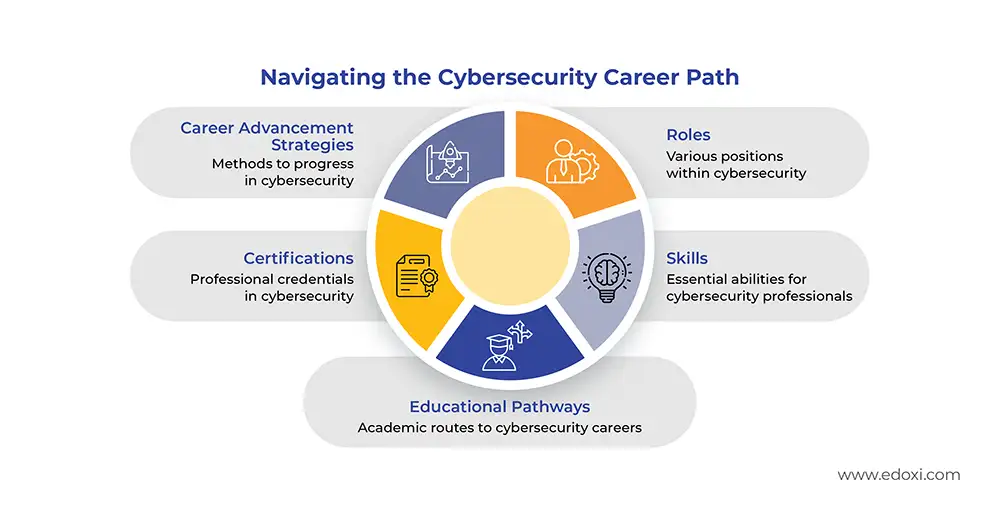
Navigating a cybersecurity career path involves a strategic mix of education, hands-on experience, certifications, and networking, allowing professionals to progressively advance from entry-level to senior leadership roles. Understanding the typical career progression and continuously updating skills are key to long-term success. Cyber security courses are the best resource to hone your cybersecurity skills and land in a high-paying job role.
Entry-level cybersecurity roles are foundational positions that help organizations protect their networks, systems, and data from digital threats. An entry-level professional should possess in-demand cybersecurity skills such as monitoring security breaches, responding to incidents, implementing protective measures, and supporting experienced analysts or engineers with various security tasks. Several entry-level positions serve as excellent starting points for a cybersecurity career. These roles often involve foundational tasks and provide opportunities to learn and grow within the field. Take a look at some popular Entry-level Cybersecurity job role;
Security analysts monitor networks and systems for security breaches or intrusions. They analyze security events, investigate incidents, and implement security measures to protect organizational assets. Key skills include knowledge of security tools, network protocols, and incident response procedures.
Security specialists focus on specific areas of cybersecurity, such as network security, endpoint security, or cloud security. They implement and maintain security controls, conduct vulnerability assessments, and provide security awareness Training.
IT auditors evaluate an organization's IT infrastructure and security controls to ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards. They identify vulnerabilities, assess risks, and recommend improvements to enhance security Posture.
These roles provide technical support to users while also addressing security-related issues. They may assist with password resets, malware removal, and security software installation.
Mid-level cybersecurity roles are positions for experienced professionals who have moved beyond entry-level duties, requiring deeper technical knowledge and problem-solving skills to design, implement, and manage security systems. With experience and advanced skills, cybersecurity professionals can advance to mid-level roles that involve more complex responsibilities and strategic decision-making.
Security engineers design, implement, and manage security systems and infrastructure. They develop security architectures, configure security devices, and conduct security testing. Strong technical skills and knowledge of security principles are essential.
Network security engineers specialize in securing network infrastructure, including firewalls, routers, and switches. They configure security policies, monitor network traffic, and respond to security incidents.
Security consultants provide expert advice and guidance to organizations on cybersecurity matters. They assess security risks, develop security strategies, and recommend security solutions.
Incident responders investigate and respond to security incidents, such as data breaches and malware infections. They analyze incident data, contain the damage, and restore systems to normal operation.
These professionals identify vulnerabilities in systems and applications through manual and automated testing techniques. They simulate real-world attacks to assess security weaknesses and recommend remediation measures.
Senior-level cybersecurity roles are advanced positions responsible for designing, overseeing, and continuously improving an organization’s security strategy and infrastructure. These professionals lead teams, manage incident response, conduct complex risk assessments, and ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards. To become a Senior-level cybersecurity professional, you will need extensive experience, leadership skills, and a deep understanding of cybersecurity principles and practices.
Security architects design and implement comprehensive security architectures that align with business objectives and regulatory requirements. They develop security policies, standards, and guidelines.
Security managers oversee security teams and manage security operations. They develop security budgets, manage security projects, and ensure compliance with security policies.
The CISO is responsible for the overall security of an organization's information assets. They develop and implement security strategies, manage security risks, and ensure compliance with regulations. A CISO is one of the highest-paying cybersecurity job roles globally.
Security directors lead security teams and manage security programs across multiple departments or business units. They develop security policies, manage security budgets, and ensure compliance with regulations.
|
Technical Skills |
Soft Skills |
|
|
A strong educational foundation and relevant certifications are essential for a successful cybersecurity career.
Industry-recognized certifications demonstrate expertise in specific areas of cybersecurity. Some popular certifications include:
The table below presents the average salaries for cybersecurity professionals at entry-level, mid-level, and senior-level positions. Take a look to understand the earning potential across different stages of a cybersecurity career.
|
Cybersecurity Level |
Job Roles |
Average Salary Range (Annual) |
|
Entry-Level |
Security Analyst, Security Specialist, IT Auditor |
$55,000 – $85,000 |
|
Mid-Level |
Penetration Tester, Incident Responder, Security Engineer |
$85,000 – $120,000 |
|
Senior-Level |
Security Architect, Cybersecurity Manager, CISO |
$120,000 – $200,000+ |
Read Also : Top Cybersecurity Training Companies in Iraq
A career in cybersecurity is not only financially rewarding but also offers immense growth potential in a world that increasingly relies on digital systems. From entry-level positions to senior leadership roles, each stage of the cybersecurity career path brings new challenges, responsibilities, and opportunities to make a meaningful impact. By building a solid educational foundation, earning globally recognized certifications, and continuously upgrading your skills, you can carve out a successful future in this high-demand field.
Whether your goal is to become a Security Analyst, a Penetration Tester, or a Chief Information Security Officer, the journey is filled with opportunities to learn, grow, and lead in safeguarding the digital world.

Leading Cybersecurity & Cloud Security Trainer
Maria Mehwish is a forward-thinking and knowledgeable information security leader with a strong background in building, updating, and maintaining digital protections for various organisations. As a certified CEH, CCSP, CCT, and CISSP Trainer, Maria has a proven track record of delivering innovative and immersive coursework, enhancing learning experiences for cyber threats, ethical hacking, security policy, DevSecOps, and cloud security. With excellent verbal and written communication skills, she is also adept at troubleshooting problems and building successful solutions.
Maria is a self-motivated individual with a strong sense of personal responsibility, capable of managing projects from start to finish. Her expertise in Amazon Web Services, Java/Go/Python/C++, DevSecOps, computer security, Linux, penetration testing, and risk analysis, among others, makes her a valuable asset to any organisation. Maria, a British national, is a native English speaker and has intermediate proficiency in Urdu.