 Tausifali Saiyed
Jan 20, 2026
Tausifali Saiyed
Jan 20, 2026

Deep learning is a specialised subset of machine learning, which is a subset of artificial intelligence. It mirrors the decision-making process of the human brain by using multi-layered artificial neural networks to solve complicated problems. This technology allows systems to automatically detect complex patterns and representations. It outperforms classic machine learning methods in applications like image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics. Deep learning forms the backbone of many cutting-edge AI applications, driving innovation across various industries globally.
According to Fortune Business Insights, the global deep learning market is expected to grow from $34.28 billion in 2025 to $279.60 billion by 2032, growing at an average rate of 35% per year. This shows that the deep learning market is growing quickly, reflecting high demand and widespread adoption of AI technologies across industries. It shows businesses view deep learning as vital for AI applications, driving investment and creating career opportunities.
In this detailed guide, we can analyse how Deep Learning works, its types, and how you can secure your career after a Deep Learning course.
Deep Learning is a technique within the field of machine learning that uses neural networks with many layers to automatically learn complex patterns from raw data such as images, sound, and text. Deep Learning helps in:
Deep learning works by using multi-layered artificial neural networks, inspired by the human brain, to process data and learn complex patterns. Here’s how Deep Learning works:
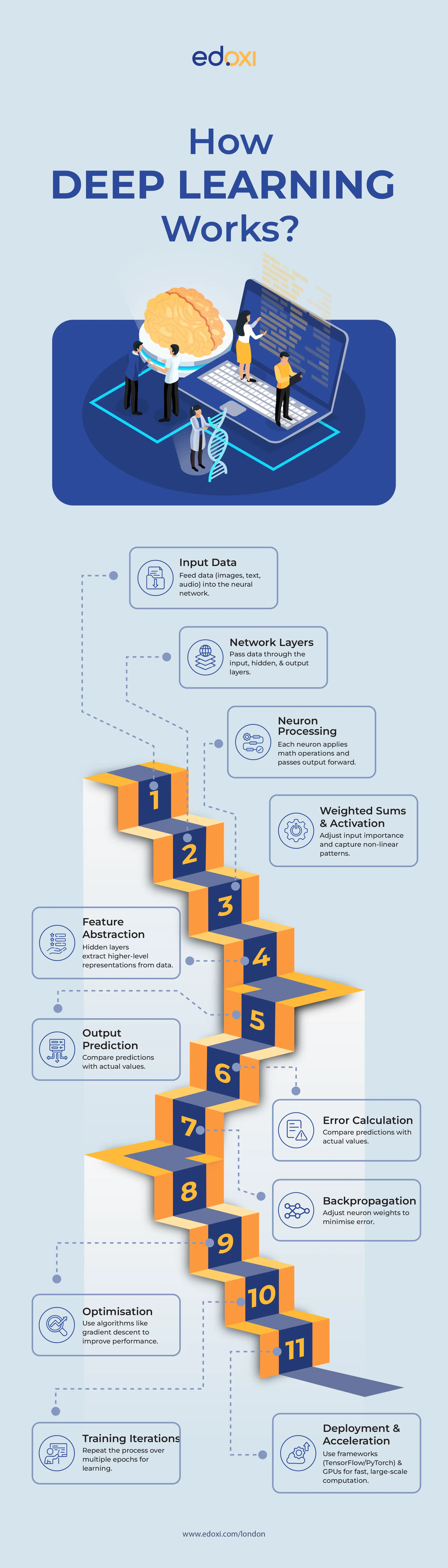
Various deep learning models are designed for specific types of data and tasks, each with unique architectural strengths. Understanding these different architectures is fundamental to applying deep learning effectively. The table below provides you with the different types of Deep Learning models.
| Deep Learning Model | What It Is | Key Strengths | Common Use Cases |
| Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) | A deep learning model designed for image and video data using convolutional layers to learn spatial features. | Detects edges, textures, and objects Learns spatial feature hierarchies automatically Highly effective for visual pattern recognition |
Image classification, object detection, facial recognition, video analysis |
| Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) | A model built for sequential or time-series data, with connections that allow information to persist. | Remembers previous sequence steps Ideal for time-dependent patterns LSTMs solve long-term dependency challenges |
Speech recognition, machine translation, sentiment analysis, text prediction |
| Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) | Foundational feedforward networks with input, hidden, and output layers. | Simple and versatile architecture Works for many prediction tasks Forms the base for advanced deep learning models |
Classification, regression, pattern recognition |
Deep Learning drives innovations in many industries by analysing complex patterns in data using neural networks with multiple layers. The common application includes
| Application Area | Use Cases / Examples |
| Computer Vision | Enables autonomous vehicles to detect obstacles, facial recognition for security, and medical imaging software to identify diseases like cancer from X-rays and MRIs. |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Powers advanced virtual assistants, real-time language translation, and generative AI tools that summarise long documents or create human-like text. |
| Healthcare | Accelerates drug discovery by predicting molecular interactions and provides personalised treatment plans based on a patient's genetic profile. |
| Finance | Used for high-frequency trading, automated fraud detection by identifying unusual transaction patterns, and credit risk assessment. |
| Recommendation Systems | Drives the suggestion engines for platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and Amazon by analysing user behaviour to predict preferences. |
| Robotics | Improves the dexterity and decision-making capabilities of industrial robots, allowing them to perform intricate tasks in manufacturing and logistics. |
| Penetration Tester | Information Technology |
Completing a deep learning course opens doors to highly sought-after roles in the rapidly expanding AI and technology sectors. Professionals equipped with deep learning skills are in high demand in job roles that include:
After completing a deep learning course, several career paths with attractive salary prospects become available, reflecting the high demand for these specialised skills. The wage for deep learning professionals can vary based on experience, specific job role, the company, and the industry. Here, the table below shows the salary of professional according to their job roles:
| Job Roles | Average Salary (USD) |
| Deep Learning Engineer | $132,131 |
| Deep Learning Research Analyst | $128,373 |
| Machine Learning Engineer | $124,237 |
| NLP Engineer | $123,696 |
| Security Auditor | Tech Companies |
| Forensic Expert | Media |
| Penetration Tester | Information Technology |
Deep learning stands at the forefront of artificial intelligence, enabling machines to understand and interact with the world in increasingly sophisticated ways. Its ability to automatically learn from complex data has revolutionised fields from healthcare to finance, powering innovations that were once considered futuristic. As AI continues its rapid advancement, expertise in deep learning, neural networks, and frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch will be crucial for future tech professionals. By mastering these skills, individuals can contribute to groundbreaking developments and secure rewarding careers in a technology-driven future.
1. What is the difference between deep learning and machine learning?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to learn from data, often without human intervention for feature extraction. Machine learning is a broader field encompassing various algorithms that learn from data to make predictions or decisions.
2. What are the key components of a deep learning model?
Key components include artificial neural networks (with input, hidden, and output layers), activation functions, optimisation algorithms (e.g., gradient descent), and loss functions.
3. Which programming languages and tools are commonly used in deep learning?
Python is the most common language, along with frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras. Libraries such as NumPy and Pandas are also essential. Hardware like GPUs is often used for accelerated training.
4. What are some real-world applications of deep learning?
Deep learning is applied in self-driving cars (object detection), voice assistants (speech recognition), medical diagnosis (image analysis), financial fraud detection, and personalised recommendations, among many others.

Full stack developer
Tausifali Sayed is an experienced full-stack developer and corporate trainer with over a decade of expertise in the field. He specialises in both the education and development of cutting-edge mobile and web applications. He is proficient in technologies including Core Java, Advanced Java, Android Mobile applications, and Cross-Platform Applications. Tausifali is adept at delivering comprehensive training in full-stack Web App Development, utilising a variety of frameworks and languages such as Java, PHP, MERN, and Python.
Tausifali holds a Master of Science (M.Sc.) in Computer Science from the University of Greenwich in London and a Bachelor of Engineering in Computer Engineering from Sardar Patel University in Vallabh Vidyanagar, India. Tausifali possesses a diverse skill set that includes expertise in Python, Flutter Framework, Java, Android, Spring MVC, PHP, JSON, RESTful Web Services, Node, AngularJS, ReactJS, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, jQuery, and C/C++. Fluent in English and Hindi, Tausifali is a versatile professional capable of delivering high-quality training and development in the IT industry.