Edoxi delivers a comprehensive CompTIA A+ certification training program in Kuwait, designed to build a strong foundation for a successful IT career. As an authorised CompTIA delivery partner, we adhere to global training standards and provide a high-quality, industry-aligned learning experience. This intensive 40-hour program develops essential competencies in hardware, software, networking, and security, preparing participants for IT support and system administration roles.
The course emphasises practical, hands-on learning through guided labs and real-world scenarios. Participants gain experience in hardware troubleshooting, PC assembly, operating system installation, and basic network setup. The curriculum is fully aligned with the latest CompTIA A+ Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) exam objectives. Our training ensures that learners acquire job-ready skills that meet current industry requirements in Kuwait. Our CompTIA A+ Course in Kuwait is available in online, classroom, and corporate training formats.
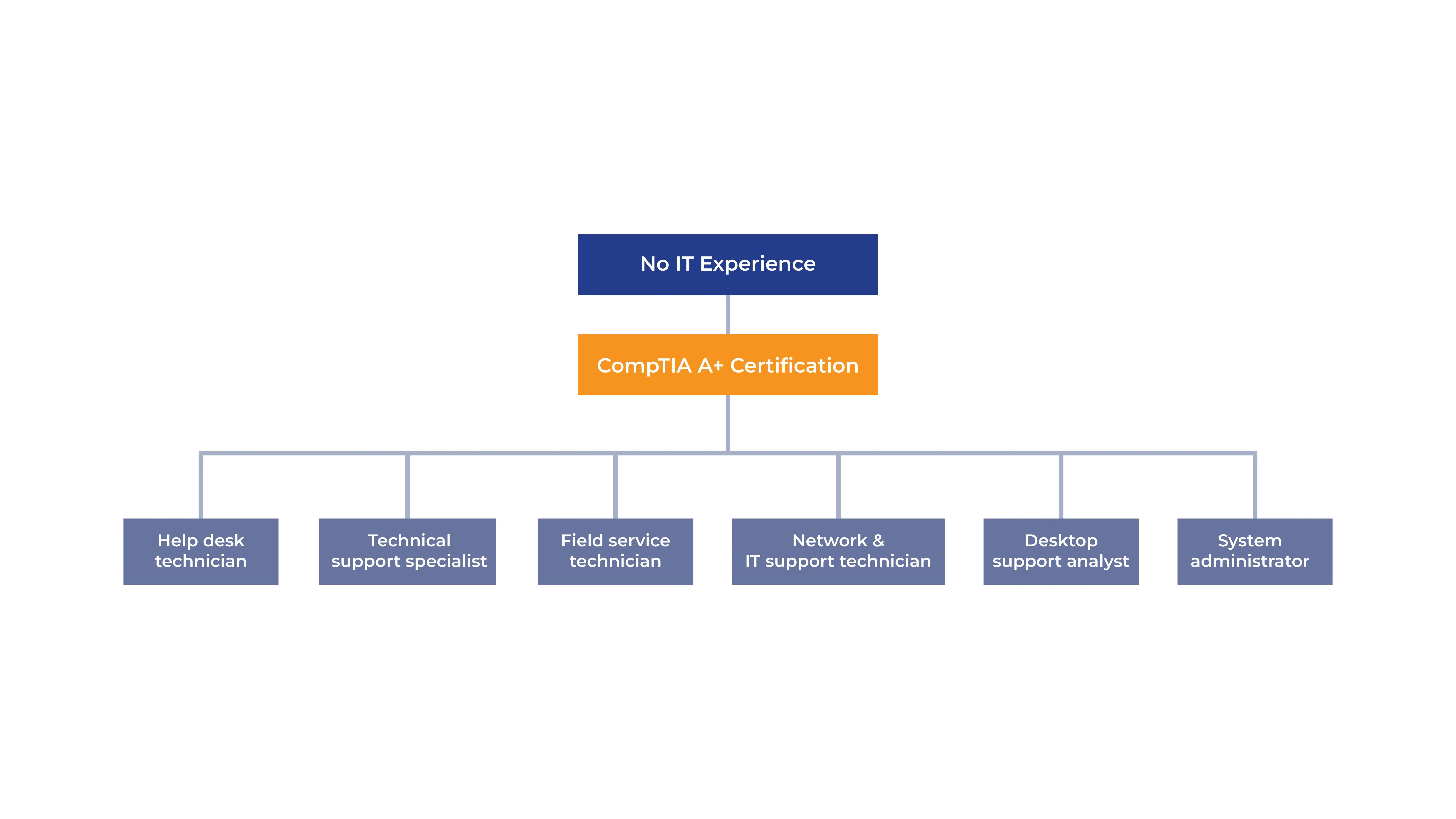
This CompTIA A+ is a vendor-neutral certification ideal for aspiring IT professionals, fresh graduates, and career changers. This globally recognised credential validates foundational skills in IT support and administration and is widely respected by employers across industries. It requires no prior IT experience and is accessible to anyone with basic computer literacy and a passion for technology. The CompTIA A+ training opens up jobs like a help desk technician, a Technical support specialist, and a system administrator across finance, healthcare, retail, hospitality, government, and education sectors.
The CompTIA A+ Certification is earned by successfully passing both required exams: Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2(220-1102) exams. The test is administered through authorised Pearson VUE testing centers. The exams assess a candidate’s ability to support, configure, and troubleshoot hardware, software, operating systems, networking, and security issues in real-world IT environments. Key exam details include;
| Exam Criteria | Details |
| Exam Code | Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) |
| Exam Duration | 90 minutes per exam |
| Number of Questions | 90 questions per exam |
| Question Types |
Multiple-choice, drag-and-drop, performance-based
|
| Passing Score | Core 1: 675/900, Core 2: 700/900 |
| Exam Fees | USD 253 + Taxes per exam |
| Certification Validity | 3 years |
| Exam Administration | Pearson VUE (online with proctoring or in-person) |
Experience hands-on hardware training by building and troubleshooting complete computer systems using professional diagnostic tools and BIOS utilities.
Practice step-by-step installation and configuration of Windows operating systems, with basic coverage of Linux and macOS environments.
Configure and test network settings using essential tools like ipconfig, while learning proper implementation of routers, switches, and firewalls.
Apply systematic troubleshooting methodologies through real-world scenarios, covering hardware, software, and network issues as outlined in Core 1 Domain 5.
Learn to implement and configure essential security tools, including antivirus software, firewalls, and encryption protocols.
Access detailed PDF study materials covering all exam objectives for both Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) certifications.
Individuals looking to start their career in IT support and administration. No prior IT experience is required, making it an ideal entry point into the technology industry.
Recent graduates seeking to build a foundation in IT infrastructure and support. Basic computer literacy provides sufficient groundwork to begin the certification journey.
Professionals from various backgrounds wanting to move into IT roles. The course structure accommodates those with basic computer operation knowledge.
Current helpdesk technicians and support specialists aiming to validate their skills and advance their careers through industry-recognised certification.
Individuals with a passion for technology and basic computer literacy looking to gain comprehensive knowledge in hardware, software, and networking.
Those planning to pursue advanced CompTIA certifications like Network+ or Security+, using A+ as their foundational stepping stone.
At Edoxi, we emphasise practical learning for our CompTIA A+ training program. Our hands-on labs focus on complete PC assembling training, where students physically build and troubleshoot computer systems. Activities include;
Build and configure a fully functional computer system from individual components. Apply proper assembly techniques, cable management, and hardware testing procedures.
Design and set up a small office network environment. Configure routers and switches, set up Wi-Fi networks.
Perform complete operating system installations and customisations. Configure drivers, security settings, and optimise the system for specific use cases.
The CompTIA A+ certification opens doors to diverse IT career opportunities across Kuwait’s technology sector. It provides a proven foundation for progression from entry-level positions to specialised technical roles, with opportunities spanning multiple industries and organisational types. Outcomes include;

Get expert assistance in getting your CompTIA A+ Course customised!
Here’s a four-step guide to becoming a certified CompTIA A+ professional.
Edoxi is one of the leading CompTIA A+ training institutes in Kuwait. Here are a few reasons why you should choose Edoxi for CompTIA A+ training in Kuwait. Here are a few reasons why you should choose Edoxi for the CompTIA A+ Course in Kuwait;
Authorised training partner with certification-aligned curriculum mapped to the latest Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) objectives.
Hands-on experience in hardware labs, including PC assembly, network configuration, and real-world troubleshooting.
Structured learning path with study materials and resources for beginners and career changers.
Flexible training options, including online and corporate formats, with a 40-hour adaptable curriculum.
Certified IT professionals with expertise in hardware troubleshooting, network configuration, and security.

Our mentors are leaders and experts in their fields. They can challenge and guide you on your road to success!

Sid Ahmed
Sid Ahmed is an IT network infrastructure and security trainer with over 12 years of experience at Edoxi Training Institute, Dubai. He is a certified CCNA/CCNP instructor and NSE 4 trainer and possesses advanced expertise in Cisco networking His portfolio includes prestigious Cisco certifications and hands-on knowledge of global security frameworks, making him a leader in delivering industry-relevant training.
Sid’s knowledge also extends to industry standards such as ISO 27001, NIST, SOC2, and PCI DSS, further strengthening his cybersecurity prowess.Sid Ahmed focuses on developing practical skills through hands-on training with enterprise-grade equipment. As an experienced Network and Security Architect, Sid Ahmed's expertise spans WAN/LAN, IP-MPLS, BGP, Wireless, IP Telephony, and Cybersecurity.He is skilled in HLD/LLD design, audits, pentesting, IT risk assessments, and security frameworks His specialisations include SD-WAN, VPN, VLAN, SSL, SIEM, cloud tech, and routing protocols (OSPF, BGP, STP) Sid is also proficient in Python, MySQL, JavaScript, APIs, and tools like SolarWinds, FortiSIEM, and U2000.
Here is the list of other major locations where Edoxi offers CompTIA A+ Certification Course
CompTIA A+ certification holds significant value in the IT industry as a vendor-neutral, globally recognised credential. The certification validates your technical skills and knowledge, enhancing your credibility and opening doors to various IT support roles with potential for career advancement.
CompTIA A+ certification is generally more accessible than CISCO's CCNA certification. While CCNA focuses specifically on Cisco networking technologies, CompTIA A+ covers broader IT concepts designed for entry-level IT professionals and those starting their technology careers.
The difficulty level depends on your background knowledge and preparation. With proper training and hands-on practice, the exams are achievable. The certification requires passing two exams (Core 1 and Core 2), each containing 90 questions, including multiple-choice and performance-based scenarios.
No prior IT experience is needed. Basic computer literacy and familiarity with common software applications provide a sufficient foundation to begin the course.
The CompTIA A+ course is available in online formats, with a duration of 40 hours. For corporate clients, we offer a concentrated 5-day training program.
Participants gain hands-on experience in hardware troubleshooting, PC assembly, operating system installations, network configuration, and IT support best practices through our dedicated lab sessions.
Graduates can pursue roles such as IT Support Technician, Help Desk Technician, Desktop Support Technician, and Computer Repair Technician.
Salaries for CompTIA A+ professionals in Kuwait are around 400 KWD to over 1,000 KWD monthly, depending heavily on experience, employer, and the specific job. Entry-level being lower and experienced roles hitting higher figures like 1,400 KWD for Technical Support Engineers or more for specialised roles