Edoxi’s 40-hour CEH training in Kuwait is designed for IT and cybersecurity professionals. It helps you develop job-ready offensive and defensive security skills using the latest AI-driven tools. As an EC-Council Accredited Training Center, Edoxi delivers globally recognised ethical hacking training aligned with industry standards. The course is ideal for individual learners and corporate teams, helping organisations strengthen cybersecurity capabilities. You can choose online training for remote learning or corporate training tailored for your team. This flexibility ensures training fits your schedule and business needs.
During this CEH certification course, you learn through hands-on, lab-based training using EC-Council’s official iLab platform. The training environment includes unpatched systems and vulnerable applications. This allows you to safely practise real-world attack and defence techniques. You gain practical exposure to the five core phases of ethical hacking to develop a structured and professional hacking methodology.
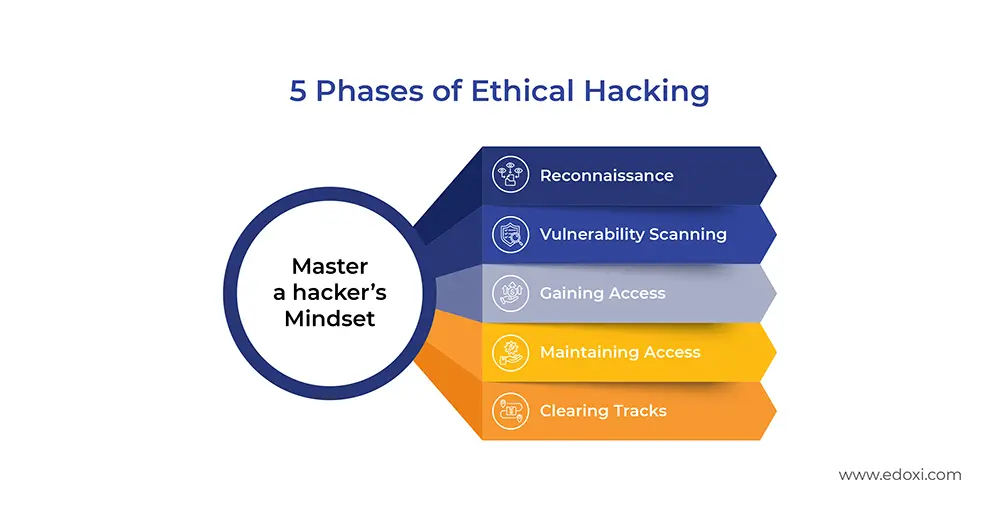
Our CEH training in Kuwait integrates advanced AI tools from EC-Council’s latest CEH v13 curriculum, enhancing your ethical hacking expertise.
| AI Tool | Application in Ethical Hacking |
| ShellGPT | • Command-line automation for penetration testing • Rapid exploit development • Automated security assessment workflows |
| ChatGPT | • Security report generation • Threat intelligence analysis • Code vulnerability assessment |
| FraudGPT | • Advanced social engineering detection • Fraud pattern recognition • Automated threat modelling |
| WormGPT | • Malware behaviour analysis • Automated vulnerability scanning • Security control testing |
| DeepExploit | • Zero-day vulnerability discovery • Exploit automation • Advanced penetration testing |
Here are the CEH v13 certification exam details.
| Component | Knowledge-Based Exam | Practical Exam (Optional) |
| Exam Code | 312-50 (ECC/VUE) | Via ASPEN iLabs |
| Duration | 4 hours | 6 hours |
| Format | 125 multiple-choice questions | Hands-on practical assessments |
| Passing Criteria | 60%–85% (varies by question weight) |
At least 50% of practicals have been successfully completed
|
| Certification | CEH v13 | CEH Master designation |
| Validity | 3 years | 3 years |
| Recertification | 120 CECs or retake the exam | 120 CECs or retake the exam |
You can train on EC-Council's iLab platform with live networks and real vulnerabilities in a secure setting.
You can engage in scenarios replicating threats like APTs, malware, and network breaches to develop practical skills.
You can complete structured exercises like password cracking and exploit testing. You can also use AI-powered tools for tasks such as vulnerability scanning and malware analysis.
You learn attacker and defender methodologies to secure systems and mitigate threats effectively.
You can analyse notable cyberattacks to understand vulnerabilities, attack vectors, and response strategies.
You learn to identify, analyse, and respond to cybersecurity incidents using advanced tools and methodologies.
If you are a network administrator, system engineer, or IT infrastructure specialist, and want to enhance your career with advanced ethical hacking and AI-driven security skills.
If you are a security analyst, ethical hacker, or cybersecurity specialist who wants to upgrade your expertise with the latest AI-powered tools and techniques.
If you have basic IT knowledge and an interest in cybersecurity, and want to build a strong foundation for a career in ethical hacking.
If you are a professional interested in transitioning to cybersecurity, and want to develop essential skills and industry-recognised credentials through this comprehensive program.
If you are a technical professional working in software development who wants to expand your security expertise to build and maintain secure applications.
If you are responsible for security audits and compliance, and want to gain hands-on technical skills for more effective security assessments.
CEH training in Kuwait offers immersive, hands-on sessions with EC-Council’s iLab platform, live networks, and pre-configured environments. These include:
In this exercise, you can access EC-Council's iLab platform with live networks and unpatched systems. You can also perform vulnerability analysis and penetration testing in secure, pre-configured environments.
In this activity, you can simulate real-world cybersecurity challenges, including SIEM systems management and Zero Trust Architecture implementation.
In this activity, you can role-play attacker and defender perspectives while analysing historical cyber-attacks. You can also develop skills in threat detection and incident response.
In this exercise, you can master tools like Nmap, Nessus, and Wireshark for network scanning. You can also perform vulnerability assessments using Burp Suite, Acunetix, and OWASP ZAP.
In this exercise, you can use advanced tools like ShellGPT for penetration testing, FraudGPT for threat detection, and DeepExploit for vulnerability assessment.
: In this project, you can complete real-world projects in penetration testing, malware analysis, cloud security, IoT assessments, and incident response.
CEH training in Kuwait offers immersive, hands-on labs and practical exercises on EC-Council’s iLab platform. These include:

Get expert assistance in getting you CEH Course customised!
Here’s a four-step guide to becoming a certified CEH professional.
Join Edoxi’s CEH Course
Edoxi’s 40-hour online CEH training in Kuwait provides practical, industry-recognised cybersecurity expertise to help you confidently achieve CEH certification. Here are the major reasons to choose us:
Edoxi is recognised as EC-Council ATC of the Year for 2023 and 2024, showcasing our excellence in cybersecurity education.
Structured learning, expert guidance, and hands-on practice sessions in Edoxi are designed to ensure your success in the CEH certification exam.
You can benefit from our discounted CEH exam vouchers and special rates for the practical certification exam.
You can practice in Edoxi’s cloud labs featuring real-world scenarios, pre-configured security tools, and exploitable vulnerabilities.
Edoxi follow EC-Council’s official curriculum, enhanced with AI tools, practical exercises, and expert instruction.
Over 10,000 professionals trained at Edoxi with a consistent record of success in certifications and career advancement.

Our mentors are leaders and experts in their fields. They can challenge and guide you on your road to success!

Satendra K
Satendra Singh Khari is a renowned cybersecurity expert and the Chief Technology Officer at Edoxi, where he leads the CEH v13 AI program. With over 12 years of experience, he has trained more than 10,000 professionals and earned recognition in the Circle of Excellence for 2023 and 2024. Mr. Khari holds multiple industry certifications, including CISSP, CISM, CEH, CPENT, and CREST, which showcase his expertise in vulnerability assessment, penetration testing, and incident handling.
His practical insights, gained during his tenure as Head of Information Security in Malaysia, enhance the learning experience by providing students with essential technical skills and a clear path to career advancement. Recognized as a leader in his field, he has received the Internet 2.0 Outstanding Leadership Award for three consecutive years (2022-2024), reflecting his dedication to empowering the next generation of cybersecurity professionals.
Here is the list of other major locations where Edoxi offers CEH Course
Edoxi’s CEH course integrates AI into all phases of ethical hacking. It automates tasks, improves efficiency by up to 40%, and provides extensive hands-on practice to strengthen your defensive and offensive cybersecurity skills.
No prior ethical hacking experience is needed. Helpful prerequisites for you include:
Yes. Edoxi’s CEH course aligns with EC-Council’s exam objectives. You gain hands-on practice, complete exam-oriented scenarios, and attempt mock tests that prepare you to pass the CEH knowledge-based exam (312-50) and the CEH (Practical) exam via ASPEN iLabs for the CEH Master credential.
You gain expertise in ethical hacking fundamentals, AI-powered tools, vulnerability assessment, system hacking, web and mobile security, and advanced scanning techniques through practical labs and real-world simulations.