Edoxi’s Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) v13 Training in Sydney provides learners with advanced skills to identify, exploit, and secure vulnerabilities in digital systems. It is specifically designed to equip cybersecurity professionals, IT specialists, and ethical hacking enthusiasts. The CEH course follows the official EC-Council CEH v13 curriculum. Our training blends theory with intensive practical sessions to help learners understand how cyberattacks are carried out and how to defend against them.
There is a growing demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals in Sydney’s rapidly expanding technology sector. Edoxi’s CEH training in Dubai provides the knowledge and hands-on experience required to excel in this high-demand field. The training empowers professionals to tackle industry-specific cybersecurity challenges with advanced AI tools and technologies.
Edoxi’s CEH v13 course provides comprehensive lab-based training through EC-Council's iLab platform. The training environment features unpatched systems and vulnerable applications, enabling you to practice ethical hacking techniques in a controlled setting.
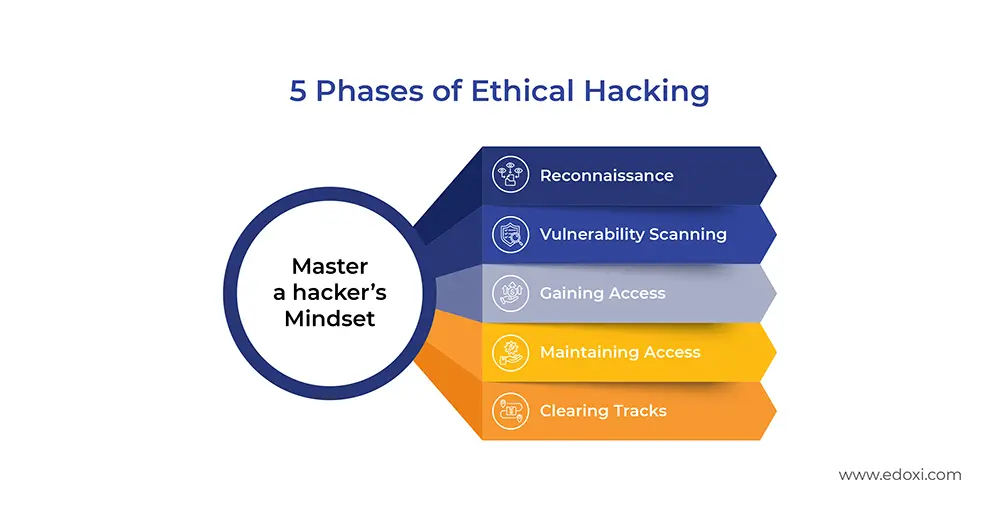
During our course, you will learn all five phases of ethical hacking, including Reconnaissance, Vulnerability Scanning, Gaining Access, Maintaining Access, and Clearing Tracks. These 5 steps provide a structured approach to identifying, exploiting, and securing vulnerabilities, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of offensive and defensive cybersecurity strategies.
Edoxi’s CEH V13 Course in Sydney includes guided exercises and real-world simulations. Participants develop practical cybersecurity skills that align with industry requirements. Our training integrates advanced AI tools from EC-Council’s latest CEH v13 curriculum, enhancing your ethical hacking expertise. The following table showcases all the AI tools that you will be learning.
| AI Tool | Application in Ethical Hacking |
| ShellGPT |
|
| ChatGPT |
|
| FraudGPT |
|
| WormGPT |
|
| DeepExploit |
|
EC-Council’s CEH v13 Exam Details
Our CEH v13 AI training in Sydney will help you prepare for the CEH v13 Certification exam. Additionally, we offer dual certification opportunities to validate your expertise in ethical hacking: the EC-Council Certification and the Edoxi Course Completion Certificate. The Certification exam details include;
| Component | Knowledge-Based Exam | Practical Exam (Optional) |
| Exam Code | 312-50 (ECC/VUE) | Via ASPEN iLabs |
| Duration | 4 hours | 6 hours |
| Format | 125 multiple-choice questions | Hands-on practical assessments |
| Passing Criteria | 60%–85% (varies by question weight) | At least 50% of the practicals have been completed |
| Certification | CEH v13 | CEH Master designation |
| Validity | 3 years | 3 years |
| Recertification | 120 CECs or retake the exam | 120 CECs or retake exam |
Get training in EC-Council's iLab platform with live networks and real vulnerabilities in a secure setting.
Engage in scenarios replicating threats like APTs, malware, and network breaches to develop practical skills.
Complete structured exercises like password cracking and exploit testing. Use AI-powered tools for tasks such as vulnerability scanning and malware analysis.
Learn attacker and defender methodologies to secure systems and mitigate threats effectively.
Analyse notable cyberattacks to understand vulnerabilities, attack vectors, and response strategies.
Learn to identify, analyse, and respond to cybersecurity incidents using advanced tools and methodologies.
Network administrators, system engineers, and IT infrastructure specialists can enhance their careers with advanced ethical hacking and AI-driven security skills.
Security analysts, ethical hackers, and cybersecurity specialists can upgrade their expertise with the latest AI-powered tools and techniques.
Those with basic IT knowledge and an interest in cybersecurity can build a strong foundation for a career in ethical hacking.
Professionals interested in transitioning to cybersecurity can develop essential skills and industry-recognised credentials through this comprehensive program.
Technical professionals working in software development can expand their security expertise to build and maintain secure applications.
Those responsible for security audits and compliance can gain hands-on technical skills for more effective security assessments.
The CEH v13 Course in Sydney, Australia emphasises practical learning through hands-on projects and case studies. These exercises give students real-world experience in ethical hacking, helping them apply cybersecurity concepts to realistic attack and defence scenarios. Here are some of the projects and case studies in our course;
Learners perform a penetration test on a simulated vulnerable web application. They will identify and exploit common vulnerabilities like SQL injection and XSS, then prepare a professional security report with recommendations.
Students simulate attacks on a virtual network to identify weaknesses and gain unauthorised access. After the attack phase, they will secure the network by patching vulnerabilities and applying defence strategies.
Get access to EC-Council's iLab platform with live networks and unpatched systems. Perform vulnerability analysis and penetration testing in secure, pre-configured environments.
You simulate real-world cybersecurity challenges, including SIEM systems management and Zero Trust Architecture implementation.
You master tools like Nmap, Nessus, and Wireshark for network scanning. Perform vulnerability assessments using Burp Suite, Acunetix, and OWASP ZAP.
You get to use advanced tools like ShellGPT for penetration testing, FraudGPT for threat detection, and DeepExploit for vulnerability assessment.
You complete real-world projects in penetration testing, malware analysis, cloud security, IoT assessments, and incident response.
You role-play attacker and defender perspectives while analysing historical cyber-attacks. Develop skills in threat detection and incident response.
The Certified Ethical Hacker v13 AI certification unlocks diverse career opportunities in Sydney's thriving technology sector. The following are the CEH V13 course outcomes you can expect after completing our CEH V13 training in Sydney, Australia;

Get expert assistance in getting you Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH v13 AI) Course customised!
Here’s a four-step guide to becoming a certified CEH v13 professional.
Join Edoxi’s Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH v13 AI) Course
Here are a few reasons why you should choose Edoxi for CEH V13 in Sydney, Australia;
Gain the skills and confidence to ace the CEH exam through a structured learning path, expert mentorship, and immersive hands-on practice.
Access exclusive discounts on CEH exam vouchers and enjoy special pricing for the practical certification exam.
Train in state-of-the-art cloud labs designed with real-world attack scenarios, vulnerabilities, and preconfigured security tools.
Learn through the official EC-Council curriculum, enhanced with AI-driven tools, practical exercises, and guidance from experienced instructors.
Join over 10,000 professionals who have achieved their certification goals and advanced their cybersecurity careers with Edoxi.
Top entities such as the UAE Federal Government, Emirates Digital Wallet, Australian Embassy, Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, Nigerian Government (Ministry of Foreign Affairs), The Supreme Council for National Security and Saudi Aramco rely on Edoxi for world-class cybersecurity training.

Here is the list of other major locations where Edoxi offers Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH v13 AI) Course
The CEH v13 program integrates AI into all phases of ethical hacking. It enhances task automation, improves efficiency by up to 40%, and provides extensive hands-on coverage to strengthen defensive and offensive cybersecurity skills.
No prior experience in ethical hacking is required, as our curriculum and trainers ensure that all participants make steady progress. Here are some helpful prerequisites:
Willingness to Learn: A strong interest in cybersecurity and AI-integrated tools, along with an eagerness to explore new concepts, is essential.
Certified professionals can start as Junior Security Analysts or Penetration Testers and advance to roles like Security Consultant or Network Security Engineer. The certification is highly valued across IT, banking, government, and healthcare sectors, with strong demand in Sydney.
Yes, our Certified Ethical Hacker course in Sydney is designed to align with EC-Council's exam objectives. It includes focused exam preparation, hands-on labs, and practice tests, equipping you to confidently pass the CEH certification exam.
Our Certified Ethical Hacker course includes 40 hours of comprehensive training available in online or corporate formats. We also offer flexible scheduling to accommodate working professionals.